Characterize your stream reach
Stream Channel Characterization
Channel morphology is an important component of steam metabolism influencing discharge, light availability, deposition and erosion, benthic and suspended algae biomass, and many other stream parameters. This SOP defines how to measure stream profiles,cross sections, and pebble counts at the reach scale and is designed to coincide with other StreamPULSE Protocols: benthic and necromic biomass and light availability.
Objective: Conduct 10 cross sections and pebble counts at randomly selected points along the reach length that encompass all types channel morphologies observed during a longitudinal profile (stream slope). This SOP also includes measurements needed for the biomass and necromass and light availability protocols.
Equipment
- Data sheets
- Notebooks
- Measuring tape (2)
- Meter sticks (3)
- Wading rod (2)
- Handheld GPS (2)
- Total Station or RTK GPS (when better accuracy is needed) (1)
Measurements
- Stream longitudinal profile
- Stream slope
- 10 cross sections with
- Stream width measured at the baseflow water mark level
- Stream width measured at the water level at the time of sampling
- Bank height for both banks
- Bank width for both banks
- Vertical distance between the water mark level and the water level at the time of sampling, for both banks
- 10-20 water depth measurements taken at recorded intervals across the stream
- Channel width measured at bankfull level, which is a function of stream width at the watermark and left and right bank widths
- Riparian canopy height
- Biomass and necromass
Instrument selection depends on site characteristics
- Handheld (Garmin)
- Thalweg, Open-canopy, Lots of satellites
- Level Shot or Transit Surveyor ( )
- Thalweg, cross section, stream slope
- Total Station (Trimble)
- Cross section. Better accuracy (<1m), stream slope
- RTK GPS (Trimble)
- Cross section. Closed canopy. Best accuracy (<1cm), stream slope
Definition of stream reach as defined by StreamPULSE
- Choose a reach length for in depth measurements. We are recommending that you estimate reach length for the median v and kO2 value estimated from your metabolism models for the previous year. Reach length = 3v/KO2 where v is velocity (m min-1) and KO2 is the rate of O2 exchange between the water column and the atmosphere (min-1) and where modeled median k=9.5/day
- If 3v/KO2 is unrealistic. Then use .7v/KO2
- Or 500m for 1st order streams and 1000m for 2nd and larger order streams
Channel Morphology Measurements
-Stream reach longitudinal profile - Completed during stream profile - (Light Protocol)
3-5 people
- Start at the location of your sensor array. Measure GPS point at thalweg. Measure bankfull cross section (below)
- Walk upstream to the end of the reach taking these measurements (n>20):
- GPS points at the thalweg at every major transition between pool, riffle, and runs. (n>20)
- Mark changes of pool, riffle, and run in notebook for cross section selection
- Length, width, depth of pool, riffle, and runs when feasible
- Sketch diagram of stream reach intervals
- End at reach length. Measure GPS point at thalweg. Measure bankfull cross section (below)
-Stream slope - Completed during stream profile - (Light Protocol)
2-5 people
Options
- DEM - Large rivers, 1-5m resolution
- Handheld GPS - accurate if no canopy interference
- Clinometer - Small rivers, least accurate
- Level shot survey - flat straight rivers, need accurate starting point GPS elevation
- Transit survey - Need accurate starting point GPS elevation
- Total station - Laser level, <1m resolution
- GPS RTK - Laser level, <1cm resolution
Measurements
- Thalweg/channel slope over reach length
- Slope of water’s surface over reach length
General Protocol
- Set up station where the observer can see a long stretch of water without obstruction
- Measure height of instrument and height of rod or person’s eyes
- Walk upstream marking points (n>20) at changes in slope. Be sure to mark every change in channel unit.
- Distance between the upstream and downstream elevation is the channel slope
Channel Cross Sections (Data Sheet)
2-5 people
The goal of these cross section measurements is to characterize the distribution of depths within your channel and to understand how those depths vary at different flows. This will improve estimates of channel depth and residence time.
You will select 10 locations along your reach for cross section measurement. You should distribute those 10 sites proportionally amongst your habitat types (e.g. if your reach is 60% run, 30% pool and 10% riffle you will randomly place 8 transects within the length of your runs, 3 samples within the length of your pools and 1 sample in the length of your riffles)
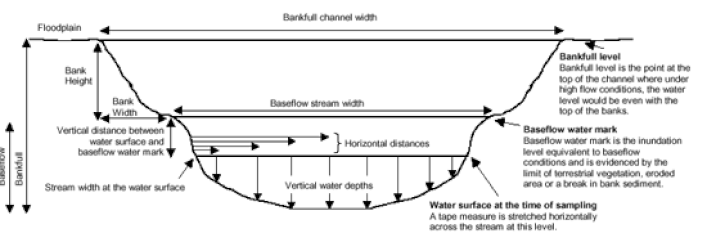
This is Figure 5.24 in Australian River Assessment System: AusRivAS Physical Assessment Protocol written by Melissa Parsons, Martin Thoms and Richard Norris and available online at https://ausrivas.ewater.org.au/protocol/chapter5n.html
Option 1: Tape measure and meter stick method (recommended where applicable)
Option 2: Level Shot or Transit Survey (Ask around other departments if you don’t have one)
Option 3: Total station method (experience necessary, ask other departments)
RTK GPS Method (Coming soon)
Optional protocols that can be completed at the same time
-Wohlman Pebble Count - Completed during cross sections - (Description) (Data Sheet)
1-2 people
-Riparian Canopy Height - Completed during cross section - (Data Sheet) (Light Protocol)
The measurement of riparian overstory canopy height is needed for developing a model to predict light conditions at the top of the stream that accounts for the geometry of the stream and surrounding landscape.
Equipment
Combined clinometer/laser range finder (Nikon Forestry Pro Laser Rangefinder
Link; $399) or separate clinometer & laser range finder
Measurements (Under Development)
The height (m) of the top of the canopy should be measured by using a clinometer and laser range finder. Measurements should be made at the same locations as the stream cross sections to facilitate generating either spatially variable or mean canopy heights (e.g. if there is a stark change in vegetation type along a reach or if there is a difference in canopy heights on opposite banks). If possible, measurement/estimation of the maximum canopy overhang and height of maximum canopy overhang should also be measured. These can be used to refine the estimation of modeled light
-Biomass & Necromass - Completed during cross section - (Data Sheet) (see Measuring Biomass Protocol)
- Define location of cross section. Identify the bankfull level, baseflow water mark, and present water level.
- Stretch a tape measure across the surface of the water from one edge of the stream to the other and secure both ends. Record the stream width at the water surface
- Record horizontal distance and vertical water depth at 10-20 points across the tape measure using a meter stick. Choose points that represent the streambed and the slope changes at the banks.
- Move back across the stream and measure bank height and bank width.
- Where necessary, also measure vertical distance between the water surface and the baseflow water mark.
- Measure stream width at the baseflow water mark using the tape measure.
- Return to the starting bank and measure bank height, bank width (Figure 5.27) and, vertical distance between the water surface and the water mark.
- Sketch the cross-sectional channel shape, including the location of bars or braids, and indicate where the bankfull and baseflow water mark levels were located.
Option 2: Level Shot or Transit Survey (Ask around other departments if you don’t have one)
- Define location of cross section. Identify the bankfull level, baseflow water mark, and present water level.
- Set up level shot survey set up on the edge of the flood plain and bank full edge looking down into the stream channel
- Measure height of rod and level shot survey. Set azimuth on level shot to 0 degrees
- Start survey. Read both top and bottom line in the cross hairs. Top line is A. Bottom line is B. The optical properties yield the distance to the rod. (A-B)*100 = horizontal distance.
- Continue taking measurements across the channel as defined above. Record bankfull level, bank height and width, baseflow mark, water level to baseflow mark, baseflow mark width, wetted width, and 10-20 water depth measurements
- Stop once the rod person has reached the other bankfull point
Option 3: Total station method (experience necessary, ask other departments)
- Define location of cross section. Identify the bankfull level, baseflow water mark, and present water level.
- Set up total station so that the rod person can be seen at across the entire bankfull cross section. Preferably on the flood plain looking down into the stream
- Measure height of rod and total station
- Backshot for reference
- Measure bankfull edge
- Measure bankfull slope change
- Measure baseflow water mark
- Measure edge of water
- Measure 10-20 points within the stream. Recording manually the water depth in a notebook
- Measure edge of water
- Measure baseflow water mark
- Measure bankfull slope change
- Measure bankfull edge
- Shoot backshot for reference
- Pack up station
RTK GPS Method (Coming soon)
Optional protocols that can be completed at the same time
-Wohlman Pebble Count - Completed during cross sections - (Description) (Data Sheet)
1-2 people
- Complete pebble count at all 10 cross sections
- Select a reach for sediment particle size distribution quantification. For stream characterization, sample pools and riffles at the same proportion the occur in the stream reach.
- Start transect at a randomly selected point (throw a pebble) along the edge of stream. Take one step into the water perpendicular to flow and, while averting your eyes, pick up the first pebble touching your index finger next to your big toe.
- Measure the b-axis by determining which hole the pebble fits through in the gravelometer and record in data book. For embedded pebbles or those that are too large to move, measure the shortest axis visible.
- Take another step across the stream and repeat the previous steps until you reach the opposite side. Establish a new transect and begin the process over again. If your stream reach is relatively narrow (<2 m), you can modify the method by walking upstream in a zig-zag pattern instead of perpendicular to flow. In general, you will need to collect 100 measurements in order to accurately quantify pebble distributions.
-Riparian Canopy Height - Completed during cross section - (Data Sheet) (Light Protocol)
The measurement of riparian overstory canopy height is needed for developing a model to predict light conditions at the top of the stream that accounts for the geometry of the stream and surrounding landscape.
Equipment
Combined clinometer/laser range finder (Nikon Forestry Pro Laser Rangefinder
Link; $399) or separate clinometer & laser range finder
Measurements (Under Development)
The height (m) of the top of the canopy should be measured by using a clinometer and laser range finder. Measurements should be made at the same locations as the stream cross sections to facilitate generating either spatially variable or mean canopy heights (e.g. if there is a stark change in vegetation type along a reach or if there is a difference in canopy heights on opposite banks). If possible, measurement/estimation of the maximum canopy overhang and height of maximum canopy overhang should also be measured. These can be used to refine the estimation of modeled light
-Biomass & Necromass - Completed during cross section - (Data Sheet) (see Measuring Biomass Protocol)